Última actualización: septiembre 5, 2022
2.3.2.3 Práctica de laboratorio: Configuración de PVST+ rápido, PortFast y protección BPDU (versión para el instructor)
Nota para el instructor: el color de fuente rojo o las partes resaltadas en gris indican texto que aparece en la copia del instructor solamente.
Topología
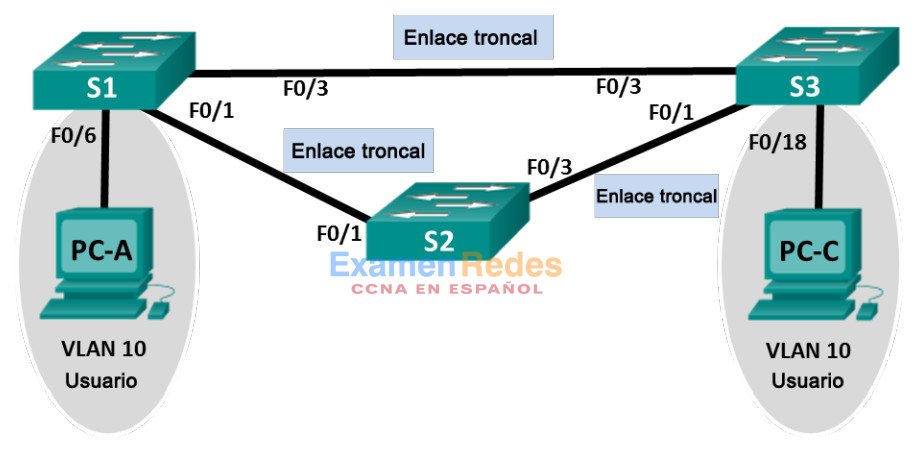
Tabla de asignación de direcciones
| Dispositivo | Interfaz | Dirección IP | Máscara de subred |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.1.11 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S2 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.1.12 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S3 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.1.13 | 255.255.255.0 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.0.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.0.3 | 255.255.255.0 |
Asignación de VLAN
| VLAN | Nombre |
|---|---|
| 10 | Usuario |
| 99 | Management |
Objetivos
Parte 1: armar la red y configurar los parámetros básicos de los dispositivos
Parte 2: Configurar redes VLAN, VLAN nativa y enlaces troncales
Parte 3: Configurar el puente raíz y examinar la convergencia de PVST+
Parte 4: Configurar el PVST+ rápido, PortFast, la protección BPDU, y examinar la convergencia
Información básica/situación
El protocolo de árbol de expansión por VLAN (PVST) es exclusivo de Cisco. Los switches Cisco funcionan con PVST de manera predeterminada. PVST+ rápido (IEEE 802.1w) es una versión mejorada de PVST+ y permite un cálculo de árbol de expansión y una convergencia más rápidos en respuesta a los cambios de topología de capa 2. PVST+ rápido define tres estados de puerto: descartar, descubrir y reenviar, y proporciona varias mejoras para optimizar el rendimiento de la red.
En esta práctica de laboratorio, configurará los puentes raíz principal y secundario, examinará la convergencia de PVST+, configurará PVST+ rápido y comparará su convergencia con la de PVST+. Además, configurará los puertos perimetrales para que pasen de inmediato al estado de reenvío mediante PortFast y evitará que los puertos perimetrales reenvíen BPDU mediante la protección BPDU.
Nota: en esta práctica de laboratorio, se proporciona la ayuda mínima relativa a los comandos que efectivamente se necesitan para la configuración. Sin embargo, los comandos requeridos se proporcionan en el apéndice A. Ponga a prueba su conocimiento e intente configurar los dispositivos sin consultar el apéndice.
Nota: los switches que se utilizan en las prácticas de laboratorio de CCNA son Cisco Catalyst 2960s con IOS de Cisco versión 15.0(2) (imagen lanbasek9). Se pueden utilizar otros switches y otras versiones del IOS de Cisco. Según el modelo y la versión de IOS de Cisco, los comandos disponibles y los resultados que se obtienen pueden diferir de los que se muestran en las prácticas de laboratorio.
Nota: asegúrese de que los switches se hayan borrado y que no tengan configuraciones de inicio. Si no está seguro, consulte al instructor.
Nota para el instructor: consulte el Manual de prácticas de laboratorio para el instructor a fin de conocer los procedimientos para inicializar y volver a cargar los dispositivos.
Recursos necesarios
• 3 switches (Cisco 2960 con IOS de Cisco versión 15.0(2), imagen lanbasek9 o similar)
• 2 computadoras (Windows 7, Vista o XP con un programa de emulación de terminal, como Tera Term)
• Cables de consola para configurar los dispositivos con IOS de Cisco mediante los puertos de consola
• Cables Ethernet, como se muestra en la topología
Parte 1: Armar la red y configurar los parámetros básicos de los dispositivos
En la parte 1, configurará la topología de la red y los parámetros básicos, como direcciones IP de la interfaz, el acceso a dispositivos y contraseñas.
Paso 1: Realizar el cableado de red tal como se muestra en la topología.
Paso 2: Configure los host del equipo.
Paso 3: Inicialice y vuelva a cargar los switches, según sea necesario.
Paso 4: Configure los parámetros básicos para cada switch.
a. Desactive la búsqueda del DNS.
b. Configure el nombre del dispositivo como se muestra en la topología.
c. Asigne cisco como la contraseña de vty y la contraseña de consola, y habilite el inicio de sesión.
d. Asigne class como la contraseña cifrada del modo EXEC privilegiado.
e. Configure logging synchronous para evitar que los mensajes de consola interrumpan la entrada de comandos.
f. Desactive todos los puertos de switch.
g. Copie la configuración en ejecución en la configuración de inicio.
Parte 2: Configurar las VLAN, la VLAN nativa y los enlaces troncales
En la parte 2, creará redes VLAN, asignará puertos de switch a las VLAN, configurará puertos de enlace troncal y cambiará la VLAN nativa para todos los switches.
Nota: los comandos requeridos para la parte 2 se proporcionan en el apéndice A. Ponga a prueba su conocimiento e intente configurar las VLAN, la VLAN nativa y los enlaces troncales sin consultar el apéndice.
Paso 1: Crear las VLAN.
Utilice los comandos correspondientes para crear las VLAN 10 y 99 en todos los switches. Asigne el nombre User a la VLAN 10 y Management a la 99.
S1(config)# vlan 10 S1(config-vlan)# name User S1(config-vlan)# vlan 99 S1(config-vlan)# name Management S2(config)# vlan 10 S2(config-vlan)# name User S2(config-vlan)# vlan 99 S2(config-vlan)# name Management S3(config)# vlan 10 S3(config-vlan)# name User S3(config-vlan)# vlan 99 S3(config-vlan)# name Management
Paso 2: Habilitar puertos de usuario en modo de acceso y asignar las VLAN.
Para el puerto F0/6 en el S1 y el F0/18 en el S3, habilite los puertos, configúrelos como puertos de acceso y asígnelos a la VLAN 10.
S1(config)# interface f0/6 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# switchport mode access S1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10 S3(config)# interface f0/18 S3(config-if)# no shutdown S3(config-if)# switchport mode access S3(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10
Paso 3: Configurar los puertos de enlace troncal y asignarlos a la VLAN 99 nativa.
Para los puertos F0/1 y F0/3 en todos los switches, habilite los puertos, configúrelos como puertos de enlace troncal y asígnelos a la VLAN 99 nativa.
S1(config)# interface range f0/1,f0/3 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S1(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2(config)# interface range f0/1,f0/3 S2(config-if)# no shutdown S2(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S2(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3(config)# interface range f0/1,f0/3 S3(config-if)# no shutdown S3(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S3(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99
Paso 4: Configurar la interfaz de administración en todos los switches.
Utilice la tabla de direccionamiento para configurar la interfaz de administración en todos los switches con la dirección IP correspondiente.
S1(config)# interface vlan 99 S1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 S2(config)# interface vlan 99 S2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 S3(config)# interface vlan 99 S3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.13 255.255.255.0
Paso 5: Verificar las configuraciones y la conectividad.
Utilice el comando show vlan brief en todos los switches para verificar que todas las VLAN estén registradas en la tabla de VLAN y que se hayan asignado los puertos correctos.
S1# show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/2, Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/7
Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11
Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15
Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19
Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23
Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
10 User active Fa0/6
99 Management active
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
S2# show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/2, Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/6
Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10
Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14
Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18
Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22
Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
10 User active
99 Management active
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
S3# show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/2, Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/6
Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10
Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14
Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/19
Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23
Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
10 User active Fa0/18
99 Management active
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
Utilice el comando show interfaces trunk en todos los switches para verificar las interfaces de enlace troncal.
S1# show interfaces trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 99
Fa0/3 on 802.1q trunking 99
Port Vlans allowed on trunk
Fa0/1 1-4094
Fa0/3 1-4094
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/1 1,10,99
Fa0/3 1,10,99
Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
Fa0/1 none
Fa0/3 1,10,99
S2# show interfaces trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 99
Fa0/3 on 802.1q trunking 99
Port Vlans allowed on trunk
Fa0/1 1-4094
Fa0/3 1-4094
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/1 1,10,99
Fa0/3 1,10,99
Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
Fa0/1 1,10,99
Fa0/3 1,10,99
S3# show interfaces trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 99
Fa0/3 on 802.1q trunking 99
Port Vlans allowed on trunk
Fa0/1 1-4094
Fa0/3 1-4094
Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain
Fa0/1 1,10,99
Fa0/3 1,10,99
Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned
Fa0/1 1,10,99
Fa0/3 1,10,99
Utilice el comando show running-config en todos los switches para verificar el resto de la configuración.
S1# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1857 bytes ! version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname S1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! interface Vlan99 ip address 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login ! end
¿Cuál es la configuración predeterminada para el modo de árbol de expansión en los switches Cisco?
El modo de árbol de expansión predeterminado es PVST+.
Verificar la conectividad entre la PC-A y la PC-C. ¿El ping se realizó correctamente?
Sí.
Si el ping no se realizó correctamente, lleve a cabo la resolución de problemas de configuración hasta que se resuelva el problema.
Nota: puede ser necesario deshabilitar el firewall de las computadoras para hacer ping entre ellas correctamente.
Parte 3: Configurar el puente raíz y examinar la convergencia de PVST+
En la parte 3, determinará la raíz predeterminada en la red, asignará las raíces principal y secundaria, y utilizará el comando debug para examinar la convergencia de PVST+.
Nota: los comandos requeridos para la parte 3 se proporcionan en el apéndice A. Ponga a prueba su conocimiento e intente configurar el puente raíz sin consultar el apéndice.
Paso 1: Determinar el puente raíz actual.
¿Qué comando permite al usuario determinar el estado del árbol de expansión de un switch Cisco Catalyst para todas las VLAN? Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
show spanning-tree
Utilice el comando en los tres switches para determinar las respuestas a las siguientes preguntas:
Nota: hay tres instancias del árbol de expansión en cada switch. La configuración predeterminada de STP en los switches Cisco es PVST+, lo que crea una instancia de árbol de expansión distinta para cada VLAN (la VLAN 1 y cualquier VLAN configurada por el usuario).
¿Cuál es la prioridad del puente del switch S1 para la VLAN 1? 32769
¿Cuál es la prioridad del puente del switch S2 para la VLAN 1? 32769
¿Cuál es la prioridad del puente del switch S3 para la VLAN 1? 32769
¿Qué switch es el puente raíz?
Las respuestas varían. En esta configuración, es el switch S3.
¿Por qué se eligió este switch como puente raíz?
De manera predeterminada, el árbol de expansión elige el puente raíz sobre la base de la dirección MAC más baja.
S1# show spanning-tree
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32769
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Cost 19
Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0cd9.96e2.3d80
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Root FWD 19 128.3 P2p
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Cost 19
Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0cd9.96e2.3d80
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Root FWD 19 128.3 P2p
Fa0/6 Desg FWD 19 128.6 P2p
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32867
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Cost 19
Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0cd9.96e2.3d80
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Root FWD 19 128.3 P2p
S2# show spanning-tree
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32769
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Cost 19
Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0cd9.96e8.6f80
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Altn BLK 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Root FWD 19 128.3 P2p
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Cost 19
Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0cd9.96e8.6f80
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Altn BLK 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Root FWD 19 128.3 P2p
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32867
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Cost 19
Port 3 (FastEthernet0/3)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0cd9.96e8.6f80
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Altn BLK 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Root FWD 19 128.3 P2p
S3# show spanning-tree
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32769
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 P2p
VLAN0010
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32778
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32778 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 10)
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 P2p
Fa0/18 Desg FWD 19 128.18 P2p
VLAN0099
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32867
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32867 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 99)
Address 0cd9.96d2.5100
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 P2p
Paso 2: Configurar un puente raíz principal y secundario para todas las VLAN existentes.
Si se elige un puente raíz (switch) por la dirección MAC, esto puede generar una configuración poco óptima. En esta práctica de laboratorio, configurará el switch S2 como puente raíz y el S1 como puente raíz secundario.
a. Configure el switch S2 como puente raíz principal para todas las VLAN existentes. Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
S2(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1,10,99 root primary
b. Configure el switch S1 como puente raíz secundario para todas las VLAN existentes. Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
S1(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1,10,99 root secondary
Utilice el comando show spanning-tree para responder las siguientes preguntas:
¿Cuál es la prioridad del puente del S1 para la VLAN 1? 28673
¿Cuál es la prioridad del puente del S2 para la VLAN 1? 24577
¿Qué interfaz de la red está en estado de bloqueo?
La interfaz F0/3 en el switch S3.
S1# show spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24577
Address 0cd9.96d2.4000
Cost 19
Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 28673 (priority 28672 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0cd9.96e8.8a00
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 15 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 P2p
S2# show spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24577
Address 0cd9.96d2.4000
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 24577 (priority 24576 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0cd9.96d2.4000
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 15 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 P2p
S3# show spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 24577
Address 0cd9.96d2.4000
Cost 19
Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0cd9.96e8.7400
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/3 Altn BLK 19 128.3 P2p
Paso 3: Cambiar la topología de capa 2 y examinar la convergencia.
Para examinar la convergencia de PVST+, creará un cambio de topología de capa 2 mientras utiliza el comando debug para controlar los eventos del árbol de expansión.
a. Introduzca el comando debug spanning-tree events en el modo EXEC privilegiado en el switch S3.
S3# debug spanning-tree events Spanning Tree event debugging is on
b. Cree un cambio de topología mediante la deshabilitación de la interfaz F0/1 en el S3.
S3(config)# interface f0/1 S3(config-if)# shutdown *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP: VLAN0001 new root port Fa0/3, cost 38 *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP: VLAN0001 Fa0/3 -> listening *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP[1]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/1 *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP: VLAN0010 new root port Fa0/3, cost 38 *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP: VLAN0010 Fa0/3 -> listening *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP[10]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/1 *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP: VLAN0099 new root port Fa0/3, cost 38 *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP: VLAN0099 Fa0/3 -> listening *Mar 1 00:58:56.225: STP[99]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/1 *Mar 1 00:58:56.242: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan1, changed state to down *Mar 1 00:58:56.242: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to down *Mar 1 00:58:58.214: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to administratively down *Mar 1 00:58:58.230: STP: VLAN0001 sent Topology Change Notice on Fa0/3 *Mar 1 00:58:58.230: STP: VLAN0010 sent Topology Change Notice on Fa0/3 *Mar 1 00:58:58.230: STP: VLAN0099 sent Topology Change Notice on Fa0/3 *Mar 1 00:58:59.220: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to down *Mar 1 00:59:11.233: STP: VLAN0001 Fa0/3 -> learning *Mar 1 00:59:11.233: STP: VLAN0010 Fa0/3 -> learning *Mar 1 00:59:11.233: STP: VLAN0099 Fa0/3 -> learning *Mar 1 00:59:26.240: STP[1]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/3 *Mar 1 00:59:26.240: STP: VLAN0001 Fa0/3 -> forwarding *Mar 1 00:59:26.240: STP[10]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/3 *Mar 1 00:59:26.240: STP: VLAN0010 sent Topology Change Notice on Fa0/3 *Mar 1 00:59:26.240: STP: VLAN0010 Fa0/3 -> forwarding *Mar 1 00:59:26.240: STP[99]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/3 *Mar 1 00:59:26.240: STP: VLAN0099 Fa0/3 -> forwarding *Mar 1 00:59:26.248: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan1, changed state to up *Mar 1 00:59:26.248: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to up
Nota: antes de continuar, utilice el resultado de debug para verificar que todas las VLAN en F0/3 hayan alcanzado el estado de reenvío y, a continuación, utilice el comando no debug spanning-tree events para detener el resultado de debug.
¿Por qué estados de puerto pasa cada VLAN en F0/3 durante la convergencia de la red?
Escucha, aprendizaje y reenvío.
Utilice la marca horaria del primer y último mensaje de depuración de STP para calcular el tiempo (hasta el segundo más cercano) que tardó la red en converger. Sugerencia: el formato de la marca horaria de la depuración es fecha hh.mm.ss:mseg.
Las respuestas pueden variar un poco, pero el tiempo de convergencia debe ser de aproximadamente 30 segundos.
Parte 4: Configurar PVST+ rápido, PortFast, la protección BPDU, y examinar la convergencia
En la parte 4, configurará PVST+ rápido en todos los switches. Configurará PortFast y la protección BPDU en todos los puertos de acceso y, a continuación, utilizará el comando debug para examinar la convergencia de PVST+ rápido.
Nota: los comandos requeridos para la parte 4 se proporcionan en el apéndice A. Ponga a prueba su conocimiento e intente configurar PVST+ rápido, PortFast y la protección BPDU sin consultar el apéndice.
Paso 1: Configurar PVST+ rápido.
a. Configure el S1 para PVST+ rápido. Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
S1(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
b. Configure S2 y S3 para PVST+ rápido.
S2(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst S3(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
c. Verifique la configuración con el comando show running-config | include spanning-tree mode.
S1# show running-config | include spanning-tree mode spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst S2# show running-config | include spanning-tree mode spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst S3# show running-config | include spanning-tree mode spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
Paso 2: Configurar PortFast y la protección BPDU en los puertos de acceso.
PortFast es una característica del árbol de expansión que realiza la transición inmediata de un puerto al estado de reenvío en cuanto se activa. Esto es útil para conectar hosts de modo que puedan comenzar a comunicarse en la VLAN instantáneamente, en lugar de esperar al árbol de expansión. Para evitar que los puertos que están configurados con PortFast reenvíen BPDU, lo que podría modificar la topología del árbol de expansión, se puede habilitar la protección BPDU. Cuando se recibe una BPDU, la protección BPDU deshabilita un puerto configurado con PortFast.
a. Configure la interfaz F0/6 en el S1 con PortFast. Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
S1(config)# interface f0/6
S1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
b. Configure la interfaz F0/6 en el S1 con la protección BPDU. Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
S1(config)# interface f0/6
S1(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
c. Configure de forma global todos los puertos que no son enlaces troncales en el switch S3 con PortFast.
Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
S3(config)# spanning-tree portfast default
d. Configure de forma global todos los puertos PortFast que no son enlaces troncales en el switch S3 con la protección BPDU. Escriba el comando en el espacio proporcionado.
S3(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
Paso 3: Examinar la convergencia de PVST+ rápido.
a. Introduzca el comando debug spanning-tree events en el modo EXEC privilegiado en el switch S3.
b. Cree un cambio de topología mediante la habilitación de la interfaz F0/1 en el switch S3.
S3(config)# interface f0/1 S3(config-if)# no shutdown *Mar 1 01:28:34.946: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up *Mar 1 01:28:37.588: RSTP(1): initializing port Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.588: RSTP(1): Fa0/1 is now designated *Mar 1 01:28:37.588: RSTP(10): initializing port Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.588: RSTP(10): Fa0/1 is now designated *Mar 1 01:28:37.588: RSTP(99): initializing port Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.588: RSTP(99): Fa0/1 is now designated *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(1): transmitting a proposal on Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(10): transmitting a proposal on Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(99): transmitting a proposal on Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(1): updt roles, received superior bpdu on Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(1): Fa0/1 is now root port *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(1): Fa0/3 blocked by re-root *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(1): synced Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(1): Fa0/3 is now alternate *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(10): updt roles, received superior bpdu on Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(10): Fa0/1 is now root port *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(10): Fa0/3 blocked by re-root *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(10): synced Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(10): Fa0/3 is now alternate *Mar 1 01:28:37.597: RSTP(99): updt roles, received superior bpdu on Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.605: RSTP(99): Fa0/1 is now root port *Mar 1 01:28:37.605: RSTP(99): Fa0/3 blocked by re-root *Mar 1 01:28:37.605: RSTP(99): synced Fa0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.605: RSTP(99): Fa0/3 is now alternate *Mar 1 01:28:37.605: STP[1]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.605: STP[10]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.605: STP[99]: Generating TC trap for port FastEthernet0/1 *Mar 1 01:28:37.622: RSTP(1): transmitting an agreement on Fa0/1 as a response to a proposal *Mar 1 01:28:37.622: RSTP(10): transmitting an agreement on Fa0/1 as a response to a proposal *Mar 1 01:28:37.622: RSTP(99): transmitting an agreement on Fa0/1 as a response to a proposal *Mar 1 01:28:38.595: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up
Utilice la marca horaria del primer y último mensaje de depuración de RSTP para calcular el tiempo que tardó la red en converger.
Las respuestas pueden variar un poco, pero el tiempo de convergencia debe ser inferior a un segundo.
Reflexión
1. ¿Cuál es el principal beneficio de utilizar PVST+ rápido?
PVST+ rápido disminuye el tiempo de convergencia de capa 2 de forma considerable en comparación con PVST+.
2. ¿Cómo se logra una convergencia más rápida configurando un puerto con PortFast?
PortFast permite que un puerto de acceso pase de inmediato al estado de reenvío, lo que disminuye el tiempo de convergencia de capa 2.
3. ¿Qué es lo que protege la protección BPDU?
La protección BPDU protege el dominio de STP deshabilitando los puertos de acceso que reciben una BPDU. Las BPDU se pueden utilizar en un ataque por denegación de servicio que modifica el puente raíz del dominio y obliga a volver a calcular STP.
Apéndice A: comandos de configuración de switch
Switch S1
S1(config)# vlan 10 S1(config-vlan)# name User S1(config-vlan)# vlan 99 S1(config-vlan)# name Management S1(config-vlan)# exit S1(config)# interface f0/6 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# switchport mode access S1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10 S1(config-if)# interface f0/1 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S1(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1(config-if)# interface f0/3 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S1(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1(config-if)# interface vlan 99 S1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 S1(config-if)# exit S1(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1,10,99 root secondary S1(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst S1(config)# interface f0/6 S1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast S1(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
Switch S2
S2(config)# vlan 10 S2(config-vlan)# name User S2(config-vlan)# vlan 99 S2(config-vlan)# name Management S2(config-vlan)# exit S2(config)# interface f0/1 S2(config-if)# no shutdown S2(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S2(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2(config-if)# interface f0/3 S2(config-if)# no shutdown S2(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S2(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2(config-if)# interface vlan 99 S2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 S2(config-if)# exit S2(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1,10,99 root primary S2(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
Switch S3
S3(config)# vlan 10 S3(config-vlan)# name User S3(config-vlan)# vlan 99 S3(config-vlan)# name Management S3(config-vlan)# exit S3(config)# interface f0/18 S3(config-if)# no shutdown S3(config-if)# switchport mode access S3(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10 S3(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast S3(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable S3(config-if)# interface f0/1 S3(config-if)# no shutdown S3(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S3(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3(config-if)# interface f0/3 S3(config-if)# no shutdown S3(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S3(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3(config-if)# interface vlan 99 S3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.13 255.255.255.0 S3(config-if)# exit S3(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
Configuraciones de dispositivos, final
- Switch S1
- Switch S2
- Switch S3
S1#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1963 bytes ! version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname S1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id spanning-tree vlan 1,10,99 priority 28672 ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access spanning-tree portfast spanning-tree bpduguard enable ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! interface Vlan99 ip address 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login ! end
S2#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1864 bytes ! version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname S2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id spanning-tree vlan 1,10,99 priority 24576 ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! interface Vlan99 ip address 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login ! end
S3#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1935 bytes ! version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname S3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree portfast default spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! interface Vlan99 ip address 192.168.1.13 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login ! end
 ExamenRedes – Examen, preguntas y respuestas Redes De Computadores Examenes de Redes
ExamenRedes – Examen, preguntas y respuestas Redes De Computadores Examenes de Redes