Última actualización: abril 1, 2022
1. How does the ARP process use an IP address?
- to determine the MAC address of a device on the same network
- to determine the amount of time a packet takes when traveling from source to destination
- to determine the MAC address of the remote destination host
- to determine the network number based on the number of bits in the IP address
2. What will a host do first when preparing a Layer 2 PDU for transmission to a host on the same Ethernet network?
- It will search the ARP table for the MAC address of the destination host.
- It will query the local DNS server for the name of the destination host.
- It will initiate an ARP request to find the MAC address of the destination host.
- It will send the PDU to the router directly connected to the network.
3. Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
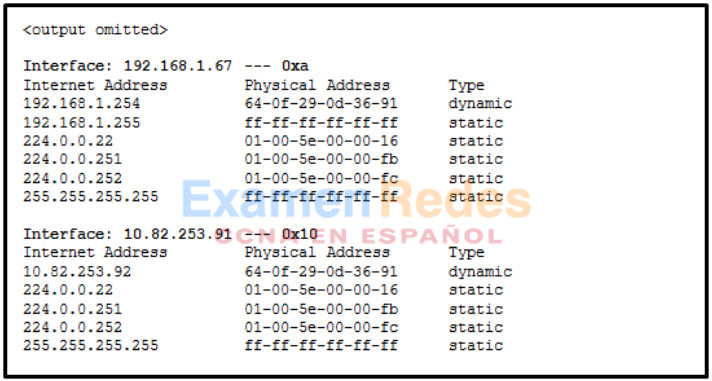
- DNS
- ICMP
- DHCP
- ARP
4. When an IP packet is sent to a host on a remote network, what information is provided by ARP?
- the MAC address of the switch port that connects to the sending host
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the router interface closest to the sending host
- the IP address of the destination host
5. A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in the ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
- It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send the frame and use the device MAC address as the destination.
6. What is the aim of an ARP spoofing attack?
- to fill switch MAC address tables with bogus addresses
- to flood the network with ARP reply broadcasts
- to associate IP addresses to the wrong MAC address
- to overwhelm network hosts with ARP requests
7. A host needs to reach another host on a remote network, but the ARP cache has no mapping entries. To what destination address will the host send an ARP request?
- the unicast MAC address of the remote host
- the unicast IP address of the remote host
- the subnet broadcast IP address
- the broadcast MAC address
8. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC2. In this scenario, what will happen next?
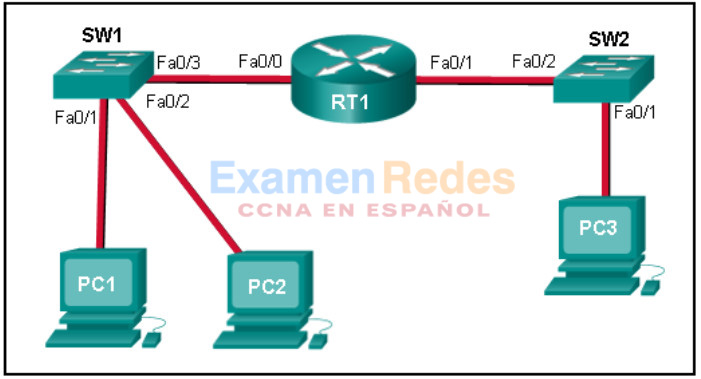
- PC2 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with the SW1 Fa0/1 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the RT1 Fa0/0 MAC address.
9. In what kind of memory is the ARP table stored on a device?
- NVRAM
- flash
- RAM
- ROM
10. What is a characteristic of ARP messages?
- ARP messages have a type field of 0x805.
- ARP messages are encapsulated within an IPv4 header.
- ARP replies are unicast.
- ARP requests are broadcasts, and they are flooded out all ports by the switch.
11. What statement describes the function of the Address Resolution Protocol?
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on the local network.
- ARP is used to discover the IP address of any host on a different network.
- ARP is used to discover the MAC address of any host on the local network.
12. Why would an attacker want to spoof a MAC address?
- so that the attacker can capture traffic from multiple VLANs rather than from just the VLAN that is assigned to the port to which the attacker device is attached
- so that a switch on the LAN will start forwarding all frames toward the device that is under control of the attacker (that can then capture the LAN traffic)
- so that a switch on the LAN will start forwarding frames to the attacker instead of to the legitimate host
- so that the attacker can launch another type of attack in order to gain access to the switch
13. What important information is examined in the Ethernet frame header by a Layer 2 device in order to forward the data onward?
- Ethernet type
- destination MAC address
- source IP address
- source MAC address
- destination IP address
 ExamenRedes – Examen, preguntas y respuestas Redes De Computadores Examenes de Redes
ExamenRedes – Examen, preguntas y respuestas Redes De Computadores Examenes de Redes