Última actualización: septiembre 8, 2022
8.1.5.5 Práctica de laboratorio: Configuración de EIGRP avanzado para admitir características de IPv4 (versión para el instructor)
Nota para el instructor: el color de fuente rojo o las partes resaltadas en gris indican texto que aparece en la copia del instructor solamente.
Topología
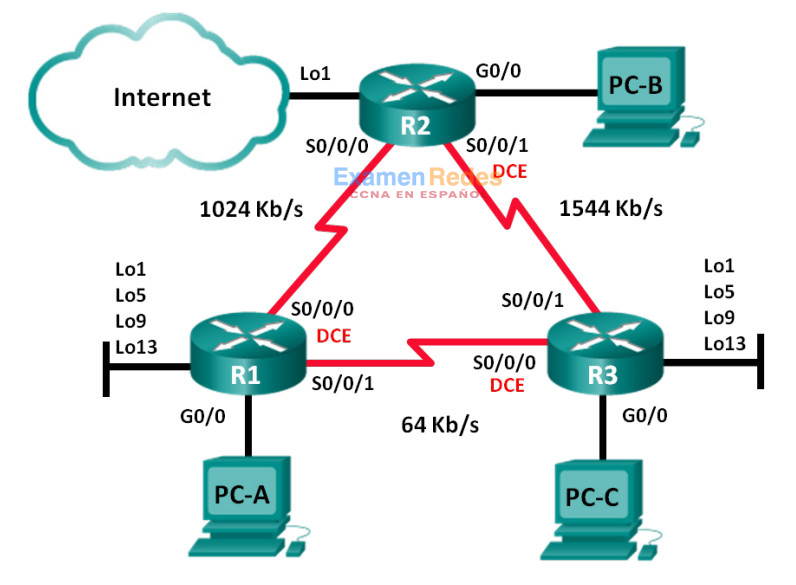
Tabla de asignación de direcciones
| Dispositivo | Interfaz | Dirección IP | Máscara de subred | Gateway predeterminado |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 (DCE) | 192.168.12.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.13.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo1 | 192.168.11.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo5 | 192.168.11.5 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo9 | 192.168.11.9 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo13 | 192.168.11.13 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R2 | G0/0 | 192.168.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.12.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 (DCE) | 192.168.23.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo1 | 192.168.22.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R3 | G0/0 | 192.168.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 (DCE) | 192.168.13.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.23.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo1 | 192.168.33.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo5 | 192.168.33.5 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo9 | 192.168.33.9 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo13 | 192.168.33.13 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.2.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.1 |
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.3.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.3.1 |
Objetivos
Parte 1: armar la red y configurar los parámetros básicos de los dispositivos
Parte 2: configurar EIGRP y verificar la conectividad.
Parte 3: Configurar la sumarización para EIGRP
• Configurar EIGRP para la sumarización automática.
• Configurar la sumarización manual para EIGRP.
Parte 4: Configurar y propagar una ruta estática predeterminada
Parte 5: Ajustar EIGRP
• Configurar el uso de ancho de banda para EIGRP.
• Configurar el intervalo de saludo y el temporizador de espera para EIGRP.
Parte 6: Configurar la autenticación de EIGRP
Información básica/situación
EIGRP tiene características avanzadas que permiten efectuar cambios relacionados con la sumarización, la propagación de rutas predeterminadas, la utilización del ancho de banda, las métricas y la seguridad.
En esta práctica de laboratorio, configurará la sumarización automática y manual para EIGRP, configurará la propagación de rutas EIGRP, ajustará las métricas de EIGRP y usará la autenticación MD5 para proteger la información de routing EIGRP.
Nota: los routers que se utilizan en las prácticas de laboratorio de CCNA son routers de servicios integrados (ISR) Cisco 1941 con IOS de Cisco versión 15.2(4)M3 (imagen universalk9). Pueden utilizarse otros routers y otras versiones del IOS de Cisco. Según el modelo y la versión de IOS de Cisco, los comandos disponibles y los resultados que se obtienen pueden diferir de los que se muestran en las prácticas de laboratorio. Consulte la tabla Resumen de interfaces del router al final de la práctica de laboratorio para obtener los identificadores de interfaz correctos.
Nota: asegúrese de que los routers se hayan borrado y no tengan configuraciones de inicio. Si no está seguro, consulte al instructor.
Nota para el instructor: consulte el Manual de prácticas de laboratorio para el instructor a fin de conocer los procedimientos para inicializar y volver a cargar los dispositivos.
Recursos necesarios
• 3 routers (Cisco 1941 con Cisco IOS, versión 15.2(4)M3, imagen universal o similar)
• 3 computadoras (Windows 7, Vista o XP con un programa de emulación de terminal, como Tera Term)
• Cables de consola para configurar los dispositivos con IOS de Cisco mediante los puertos de consola
• Cables Ethernet y seriales, como se muestra en la topología.
Parte 1: Armar la red y configurar los parámetros básicos de los dispositivos
En la parte 1, establecerá la topología de la red y configurará los parámetros básicos en los equipos host y los routers.
Paso 1: Realizar el cableado de red tal como se muestra en la topología.
Paso 2: Configure los host del equipo.
Paso 3: Inicialice y vuelva a cargar los routers, según sea necesario.
Paso 4: Configure los parámetros básicos para cada router.
a. Desactive la búsqueda del DNS.
b. Configure el nombre del dispositivo como se muestra en la topología.
c. Asigne cisco como la contraseña de consola y la contraseña de vty.
d. Asigne class como la contraseña del modo EXEC privilegiado.
e. Configure logging synchronous para evitar que los mensajes de consola interrumpan la entrada de comandos.
f. Configure la dirección IP incluida en la tabla de direccionamiento para todas las interfaces.
Nota: NO configure las interfaces loopback todavía.
g. Copie la configuración en ejecución en la configuración de inicio
Parte 2: Configurar EIGRP y verificar la conectividad
En la parte 2, configurará EIGRP básico para la topología y establecerá los anchos de banda de las interfaces seriales.
Nota: en esta práctica de laboratorio, se proporciona la ayuda mínima relativa a los comandos que efectivamente se necesitan para configurar EIGRP. Sin embargo, los comandos requeridos se proporcionan en el apéndice A. Ponga a prueba su conocimiento e intente configurar los dispositivos sin consultar el apéndice.
Paso 1: Configure EIGRP.
a. En el R1, configure el routing EIGRP con una ID de sistema autónomo (AS) de 1 para todas las redes conectadas directamente. Escriba los comandos que utilizó en el espacio que se incluye a continuación.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3
b. Para la interfaz LAN en el R1, deshabilite la transmisión de paquetes de saludo EIGRP. Escriba el comando que utilizó en el espacio a continuación.
R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0
c. En el R1, configure el ancho de banda de S0/0/0 en 1024 Kb/s y el ancho de banda de S0/0/1 en 64 Kb/s. Escriba los comandos que utilizó en el espacio que se incluye a continuación. Nota: el comando bandwidth solo afecta el cálculo de la métrica de EIGRP, no el ancho de banda real del enlace serial.
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 1024
R1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64
d. En el R2, configure el routing EIGRP con una ID de AS de 1 para todas las redes, deshabilite la transmisión de paquetes de saludo EIGRP para la interfaz LAN y configure el ancho de banda de S0/0/0 en 1024 Kb/s.
e. En el R3, configure el routing EIGRP con una ID de AS de 1 para todas las redes, deshabilite la transmisión de paquetes de saludo EIGRP para la interfaz LAN y configure el ancho de banda de S0/0/0 en 64 Kb/s.
Paso 2: Probar la conectividad.
Todas las computadoras deben poder hacer ping entre sí. Verifique y resuelva los problemas si es necesario.
Nota: puede ser necesario inhabilitar el firewall del equipo para hacer ping entre los equipos.
Parte 3: Configurar la sumarización para EIGRP
En la parte 3, agregará interfaces loopback al R1, habilitará la sumarización automática de EIGRP en el R1 y observará los efectos de esto en la tabla de routing del R2. También agregará interfaces loopback en el R3.
Paso 1: Configurar EIGRP para la sumarización automática.
a. Emita el comando show ip protocols en el R1. ¿Cuál es el estado predeterminado de la sumarización automática en EIGRP?
R1# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(1)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 192.168.13.1
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.1.0
192.168.12.0/30
192.168.13.0/30
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.12.2 90 00:30:16
192.168.13.2 90 00:30:16
Distance: internal 90 external 170
La sumarización automática de redes está deshabilitada.
b. Configure las direcciones de loopback en el R1.
c. Agregue las instrucciones network apropiadas al proceso EIGRP en el R1. Registre los comandos que utilizó en el espacio que se incluye a continuación.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.4 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.8 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.12 0.0.0.3
d. En el R2, emita el comando show ip route eigrp. ¿De qué manera están representadas las redes de loopback en el resultado?
R2# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/3014400] via 192.168.12.1, 00:14:58, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/2172416] via 192.168.23.2, 00:11:18, Serial0/0/1
192.168.11.0/30 is subnetted, 4 subnets
D 192.168.11.0 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.11.4 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.11.8 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.11.12 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
192.168.13.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.13.0 [90/41024000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:06:11, Serial0/0/1
[90/41024000] via 192.168.12.1, 00:06:11, Serial0/0/0
Todas las subredes se incluyen en el resultado de la tabla de routing.
e. En el R1, emita el comando auto-summary dentro del proceso EIGRP.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# auto-summary R1(config-router)# *Apr 14 01:14:55.463: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.13.2 (Serial0/0/1) is resync: summary configured *Apr 14 01:14:55.463: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.12.2 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary configured *Apr 14 01:14:55.463: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.13.2 (Serial0/0/1) is resync: summary up, remove components R1(config-router)#67: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.12.2 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary up, remove components *Apr 14 01:14:55.467: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.12.2 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary up, remove components *Apr 14 01:14:55.467: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.13.2 (Serial0/0/1) is resync: summary up, remove components
¿De qué manera cambia la tabla de routing del R2?
R2# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/3014400] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/2172416] via 192.168.23.2, 00:15:58, Serial0/0/1
192.168.11.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.11.0 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/0
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks
D 192.168.12.0/24 [90/41536000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.13.0/24 [90/41024000] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.13.0/30 [90/41024000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/1
Las redes 192.168.11.0 se resumen en el límite con clase.
Paso 2: Configurar la sumarización manual para EIGRP.
a. Configure las direcciones de loopback en el R3.
b. Agregue las instrucciones network apropiadas al proceso EIGRP en el R3.
c. En el R2, emita el comando show ip route eigrp. ¿De qué manera están representadas las redes de loopback del R3 en el resultado?
R2# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/3014400] via 192.168.12.1, 00:11:50, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/2172416] via 192.168.23.2, 00:26:35, Serial0/0/1
192.168.11.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.11.0 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:11:50, Serial0/0/0
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks
D 192.168.12.0/24 [90/41536000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:11:50, Serial0/0/1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.13.0/24 [90/41024000] via 192.168.12.1, 00:11:50, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.13.0/30 [90/41024000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:11:50, Serial0/0/1
192.168.33.0/30 is subnetted, 3 subnets
D 192.168.33.0 [90/2297856] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:19, Serial0/0/1
D 192.168.33.4 [90/2297856] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:19, Serial0/0/1
D 192.168.33.8 [90/2297856] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:19, Serial0/0/1
D 192.168.33.12 [90/2297856] via 192.168.23.2, 00:00:19, Serial0/0/1
Todas las subredes se incluyen en la tabla de routing.
d. Determine la ruta resumida EIGRP para las direcciones de loopback en el R3. Escriba la ruta resumida en el espacio que se proporciona a continuación.
192.168.33.0 255.255.255.240
e. Para las interfaces seriales en el R3, emita el comando ip summary-address eigrp 1 dirección red máscara subred para resumir manualmente las redes.
R3(config)# interface s0/0/0 R3(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.33.0 255.255.255.240 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface s0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.33.0 255.255.255.240 *Apr 14 01:33:46.433: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.13.1 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary configured *Apr 14 01:33:46.433: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.23.1 (Serial0/0/1) is resync: summary configured
¿De qué manera cambia la tabla de routing del R2?
R2# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/3014400] via 192.168.12.1, 00:21:32, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/2172416] via 192.168.23.2, 00:36:17, Serial0/0/1
192.168.11.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.11.0 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:21:32, Serial0/0/0
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks
D 192.168.12.0/24 [90/41536000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:21:32, Serial0/0/1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.13.0/24 [90/41024000] via 192.168.12.1, 00:21:32, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.13.0/30 [90/41024000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:21:32, Serial0/0/1
192.168.33.0/28 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.33.0 [90/2297856] via 192.168.23.2, 00:02:51, Serial0/0/1
Las redes 192.168.33.0 se resumen con una máscara /28.
Parte 4: Configurar y propagar una ruta estática predeterminada
En la parte 4, configurará una ruta estática predeterminada en el R2 y propagará la ruta a todos los otros routers.
a. Configure la dirección de loopback en el R2.
b. Configure una ruta estática predeterminada con una interfaz de salida Lo1.
R2(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Lo1
c. Use el comando redistribute static dentro del proceso EIGRP para propagar la ruta estática predeterminada a los otros routers participantes.
R2(config)# router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# redistribute static
d. Use el comando show ip protocols en el R2 para verificar la distribución de la ruta estática.
R2# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
Redistributing: static
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(1)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 192.168.23.1
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.2.0
192.168.12.0/30
192.168.23.0/30
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.12.1 90 00:13:20
192.168.23.2 90 00:13:20
Distance: internal 90 external 170
e. En el R1, emita el comando show ip route eigrp | include 0.0.0.0 para ver las instrucciones específicas de la ruta predeterminada. ¿De qué manera está representada la ruta estática predeterminada en el resultado? ¿Cuál es la distancia administrativa (AD) de la ruta propagada?
R1# show ip route eigrp | include 0.0.0.0 Gateway of last resort is 192.168.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0 D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/3139840] via 192.168.12.2, 00:06:27, Serial0/0/0
Como una ruta EIGRP descubierta de manera externa:
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/3139840] via 192.168.12.2, 00:06:27, Serial0/0/0
La distancia administrativa es de 170, ya que es una ruta EIGRP externa.
Parte 5: Ajustar EIGRP
En la parte 5, configurará el porcentaje del ancho de banda que puede usar una interfaz EIGRP y cambiará el intervalo de saludo y los temporizadores de espera de las interfaces EIGRP.
Paso 1: Configurar el uso de ancho de banda para EIGRP.
a. Configure el enlace serial entre el R1 y el R2 para permitir solo un 75% del ancho de banda del enlace para el tráfico EIGRP.
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 R2(config)# interface s0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75
b. Configure el enlace serial entre el R1 y el R3 para permitir un 40% del ancho de banda del enlace para el tráfico EIGRP.
Paso 2: Configurar el intervalo de saludo y el temporizador de espera para EIGRP.
a. En el R2, use el comando show ip eigrp interfaces detail para ver el intervalo de saludo y el temporizador de espera para EIGRP.
R2# show ip eigrp interfaces detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(1)
Xmit Queue PeerQ Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Se0/0/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/15 50 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 29/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 390/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 35/39
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Interface BW percentage is 75
Authentication mode is not set
Se0/0/1 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/16 50 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 34/5
Hello's sent/expedited: 382/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 31/42
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 2
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
¿Cuál es el valor predeterminado para el tiempo de saludo? 5 segundos
¿Cuál es el valor predeterminado para el tiempo de espera? 15 segundos
b. Configure las interfaces S0/0/0 y S0/0/1 en el R1 para que usen un intervalo de saludo de 60 segundos y un tiempo de espera de 180 segundos, en ese orden específico.
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 R1(config)# interface s0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180
c. Configure las interfaces seriales en el R2 y el R3 para que usen un intervalo de saludo de 60 segundos y un tiempo de espera de 180 segundos.
d. Use el comando show ip eigrp interfaces detail en el R2 para verificar la configuración.
R2# show ip eigrp interfaces detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(1)
Xmit Queue PeerQ Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Se0/0/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/15 50 0
Hello-interval is 60, Hold-time is 180
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 38/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 489/4
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 40/48
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Interface BW percentage is 75
Authentication mode is not set
Se0/0/1 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/16 50 0
Hello-interval is 60, Hold-time is 180
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 45/5
Hello's sent/expedited: 481/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 46/55
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 2
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Parte 6: Configurar la autenticación de EIGRP
En la parte 6, creará una clave de autenticación en todos los routers y configurará las interfaces del router para que usen autenticación MD5 para la autenticación de mensajes EIGRP.
Paso 1: Configurar las claves de autenticación.
a. En el R1, use el comando key chain nombre en el modo de configuración global para crear un llavero con la etiqueta EIGRP-KEYS.
R1(config)# key chain EIGRP-KEYS R1(config-keychain)# key 1 R1(config-keychain-key)# key-string cisco
b. Complete la configuración en el R2 y el R3.
c. Emita el comando show key chain. Debería obtener el mismo resultado en cada router.
Paso 2: Configurar la autenticación de enlaces EIGRP.
a. Aplique los siguientes comandos para activar la autenticación de EIGRP en las interfaces seriales en el R1.
R1# conf t R1(config)# interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS R1(config-if)# ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 R1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS R1(config-if)# ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5
b. Active la autenticación de EIGRP en las interfaces seriales en el R2 y el R3.
c. En el R2, use el comando show ip eigrp interfaces detail para verificar la autenticación.
R2# show ip eigrp interfaces detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(1)
Xmit Queue PeerQ Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Se0/0/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/23 50 0
Hello-interval is 60, Hold-time is 180
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 30/5
Hello's sent/expedited: 1163/5
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 25/34
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is md5, key-chain is "EIGRP-KEYS"
Se0/0/1 1 0/0 0/0 2 0/15 50 0
Hello-interval is 60, Hold-time is 180
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 31/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 1354/3
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 28/34
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 4
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is md5, key-chain is "EIGRP-KEYS"
Reflexión
1. ¿Cuáles son los beneficios de la sumarización de rutas?
La sumarización se puede utilizar para limitar la cantidad de anuncios de routing y el tamaño de las tablas de routing.
2. Cuando se configuran temporizadores de EIGRP, ¿por qué es importante que el valor del tiempo de espera sea igual o superior al intervalo de saludo?
Si el tiempo de espera es menor que el intervalo de saludo, la adyacencia de vecino queda inactiva.
3. ¿Por qué es importante configurar la autenticación de EIGRP?
Las actualizaciones de routers sin autenticar representan un riesgo de seguridad. Los atacantes pueden insertar información de rutas falsa en las actualizaciones del router a fin de redirigir el tráfico para que se creen bucles de routing o para enviar tráfico a través de enlaces no seguros.
Tabla de resumen de interfaces del router
| Resumen de interfaces del router | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modelo de router | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| Nota: para conocer la configuración del router, observe las interfaces a fin de identificar el tipo de router y cuántas interfaces tiene. No existe una forma eficaz de confeccionar una lista de todas las combinaciones de configuraciones para cada clase de router. En esta tabla, se incluyen los identificadores para las posibles combinaciones de interfaces Ethernet y seriales en el dispositivo. En esta tabla, no se incluye ningún otro tipo de interfaz, si bien puede haber interfaces de otro tipo en un router determinado. La interfaz BRI ISDN es un ejemplo. La cadena entre paréntesis es la abreviatura legal que se puede utilizar en los comandos de IOS de Cisco para representar la interfaz. | ||||
Apéndice A: comandos de configuración
Router R1
R1(config)# router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.4 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.8 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.12 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0 R1(config)# int s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# bandwidth 1024 R1(config-if)# int s0/0/1 R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64
R2 del router
R2(config)# router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 R2(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0 R2(config)# int s0/0/0 R2(config-if)# bandwidth 1024
R3 del router
R3(config)# router eigrp 1 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.0 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.4 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.8 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.12 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0 R3(config)# int s0/0/0 R3(config-if)# bandwidth 64
Configuraciones de dispositivos: R1, R2 y R3
- Router R1
- R2 del router
- R3 del router
R1#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2378 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! key chain EIGRP-KEYS key 1 key-string cisco ! ! redundancy ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback5 ip address 192.168.11.5 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback9 ip address 192.168.11.9 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback13 ip address 192.168.11.13 255.255.255.252 ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 bandwidth 1024 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 clock rate 2000000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 bandwidth 64 ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 40 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.1.0 network 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.11.4 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.11.8 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.11.12 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 auto-summary passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
Building configuration... Current configuration : 2223 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! key chain EIGRP-KEYS key 1 key-string cisco ! ! redundancy ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.22.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 bandwidth 1024 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 clock rate 2000000 ! ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.2.0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 redistribute static passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Loopback1 ! ! ! ! control-plane ! ! ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
R3#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2456 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname R3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! key chain EIGRP-KEYS key 1 key-string cisco ! ! redundancy ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.33.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback5 ip address 192.168.33.5 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback9 ip address 192.168.33.9 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback13 ip address 192.168.33.13 255.255.255.252 ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 bandwidth 64 ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 40 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.33.0 255.255.255.240 clock rate 2000000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252 ip authentication mode eigrp 1 md5 ip authentication key-chain eigrp 1 EIGRP-KEYS ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.33.0 255.255.255.240 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 ip summary-address eigrp 1 192.168.33.0 255.255.255.240 ! ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.3.0 network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.4 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.8 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.12 0.0.0.3 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
 ExamenRedes – Examen, preguntas y respuestas Redes De Computadores Examenes de Redes
ExamenRedes – Examen, preguntas y respuestas Redes De Computadores Examenes de Redes